Geniculate Artery Embolization (GAE)
What is Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Knee OA is a leading cause of disability and chronic pain that reduces physical activity and quality-of-life.
It affects millions of people in the US and has been on the rise due to the obesity epidemic and an aging population.
Patients with knee OA have pain for many reasons. One of the major reasons is inflammation of the synovium, which is the connective tissue lining of the knee.
Knee OA Risk Factors
Increasing age
Obesity
Prior knee trauma
Family history
Knee OA Signs & Symptoms
Knee pain that increases when you are active, but improves with rest
Joint stiffness, tenderness, swelling
Clicking, grinding, or snapping sounds with movement
Feeling of warmth in the joint
Decrease in mobility of the knee, making it difficult to get in and out of chairs or cars, use the stairs, or walk
Diagnosis
Physical exam
X-rays of the knee
MRI of the knee
What is Geniculate Artery Embolization (GAE)?
Geniculate artery embolization (GAE) is a safe, effective, and non-surgical outpatient procedure that provides immediate and long-term pain relief for patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
GAE specifically targets the inflammation involving the lining of the knee called the synovium by blocking the blood flow to this lining. This results in decreased inflammation and helps to eliminate or significantly reduce associated knee pain.
Who is a candidate for GAE?
Men and women 40 to 80 years old with knee pain due to OA.
Men and women with knee OA who have failed conservative therapy, including inflammatory medications like NSAIDs, physical therapy, and knee joint injections (steroids, PRP, Visco Supplementation, etc).
Those with knee OA who are ineligible or do not want to undergo knee replacement surgery.
GAE Procedure
The procedure is performed in an outpatient setting with local anesthesia, minimal sedation medications, no incisions, and short recovery time.
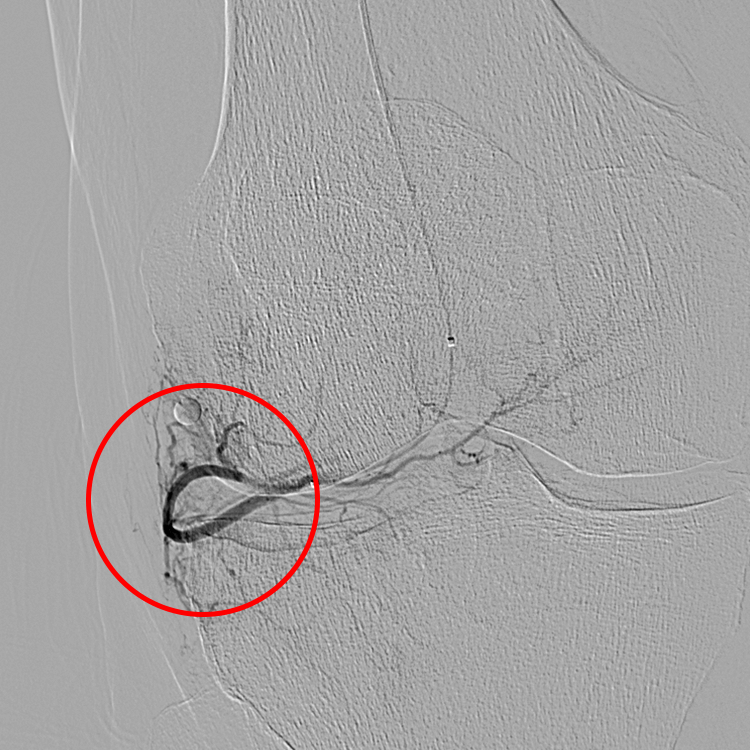
During the procedure, the physician accesses a small artery in the groin or wrist and advances a small catheter using fluoroscopy into the small arteries around the knee, which supply the synovium.
The blood flow to these small arteries is then reduced using FDA approved beads. This results in reduced inflammation in the synovium.
Pain reduction is typically noticed in 1-2 weeks and can last as long as 1 year in many patients.
After treatment and a short recovery, patients can walk out of the treatment center to go home.
Strenuous activity such as heavy lifting, weight training, biking, running, or climbing flights of stairs frequently should be avoided for 72 hours
GAE Before and After Pictures
Before treatment, there are enlarged small arteries to the inflamed lining of the knee (synovium) (red circle).
After treatment, those same small arteries are blocked off which helps to reduce inflammation in the knee lining (synovium) (green circle).

Schedule a consultation and improve your health.
Get your procedure done where you’re the center of our attention.